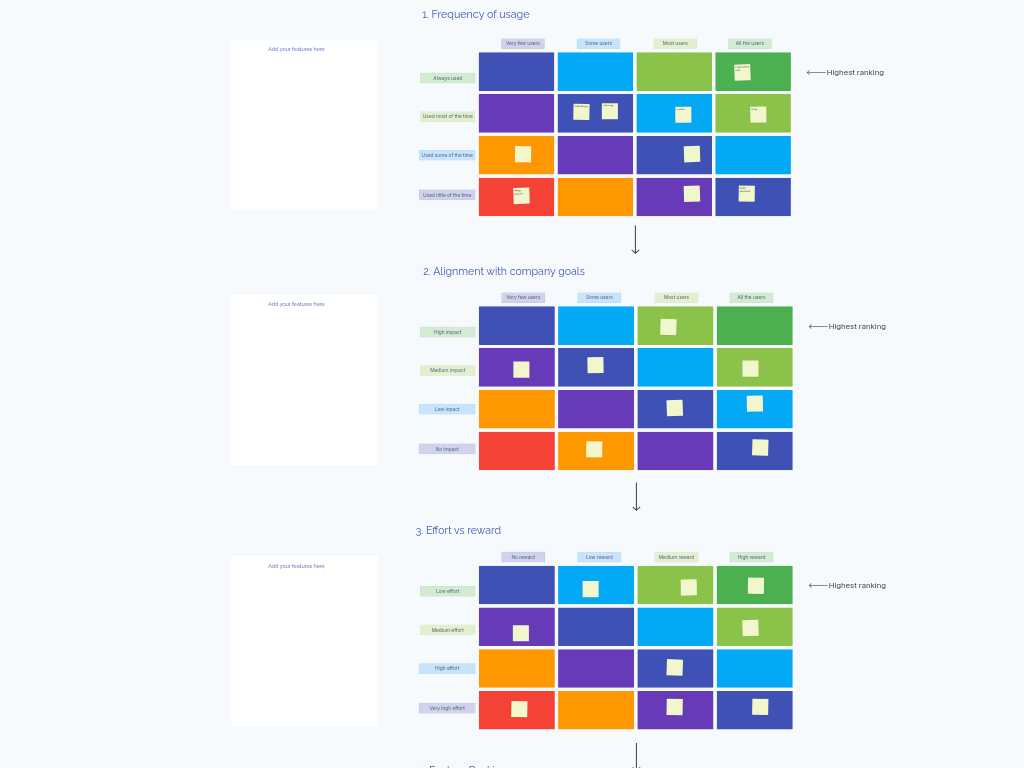
Feature Prioritization Grid
A data-driven framework that helps product and development teams systematically evaluate features across multiple dimensions to identify which ones deliver the most value with the least effort.
What Is a Feature Prioritization Grid?
The Feature Prioritization Grid is a structured decision-making tool that evaluates potential features through three critical lenses: frequency of usage, alignment with company goals, and effort-to-reward ratio. Unlike simple ranking methods, this approach creates a comprehensive view of each feature's potential impact and implementation challenges by mapping them across multiple matrices.
The grid works by visually positioning each feature according to specific criteria, making it immediately apparent which features provide the highest value. By comparing the same features across different dimensions, teams can identify patterns and make more confident prioritization decisions.
Benefits & When to Use
Use the Feature Prioritization Grid when:
- You have too many feature requests competing for limited development resources
- Your team needs to align on which features will deliver the most business value
- You want to make objective, data-informed product decisions rather than relying on opinions
- Stakeholders disagree about which features should be prioritized in your roadmap
Key benefits include:
- Reduced Decision Bias: The multi-dimensional evaluation minimizes the influence of individual preferences
- Clearer Communication: Visual positioning makes priorities immediately apparent to both technical and non-technical stakeholders
- Better Resource Allocation: Helps focus development efforts on features with the highest ROI
- Balanced Assessment: Considers both user needs and business objectives in one framework
How to Run a Feature Prioritization Grid Session
Prepare Your Feature List (10 minutes)
- Collect all feature ideas you want to evaluate
- Ensure each feature is clearly defined and understood by all participants
- Create sticky notes for each feature (you'll need three copies of each)
Set Up the Three Grids (5 minutes)
- Grid 1: Frequency of Usage (from "Always Used" to "Very Few Users")
- Grid 2: Alignment with Company Goals (from "High Impact" to "No Impact")
- Grid 3: Effort vs. Reward (from "Low Effort/High Reward" to "Very High Effort/No Reward")
Evaluate Features on Grid 1: Frequency of Usage (15 minutes)
- Position each feature based on how frequently users will engage with it
- Discuss placement as a team, particularly for features where opinions differ
- Look for patterns - features in the "Always Used" quadrant serve core user needs
Evaluate Features on Grid 2: Alignment with Company Goals (15 minutes)
- Place features according to how well they support strategic objectives
- Consider both short-term targets and long-term vision
- Features in the "High Impact" area should clearly advance key business metrics
Evaluate Features on Grid 3: Effort vs. Reward (15 minutes)
- Position features based on implementation difficulty and potential value
- Be honest about technical complexity and required resources
- The top-left quadrant (Low Effort/High Reward) represents your "quick wins"
Analyze Cross-Grid Patterns (15 minutes)
- Identify features that rank consistently high across all three grids
- Note any features with contradictory placements (e.g., high usage but low alignment)
- Create a final ranking based on where each feature appears across all grids
Document and Share Results (10 minutes)
- Record the final rankings and key insights from the discussion
- Share the prioritized list with stakeholders and the broader team
- Use the results to inform sprint planning and roadmap decisions
Tips for a Successful Session
- Involve cross-functional perspectives: Include product, engineering, design, and business stakeholders to ensure comprehensive evaluation
- Be specific about criteria: Clearly define what "high impact" or "always used" means for your specific product context
- Use data where available: Support positioning decisions with analytics, user research, or market data rather than assumptions
- Revisit periodically: Feature priorities can change as market conditions evolve, so rerun this exercise quarterly
- Focus on outcomes, not outputs: When evaluating features, consider the user and business outcomes they'll deliver, not just their technical specifications
- Keep the debate constructive: If team members disagree on positioning, focus the discussion on evidence rather than opinions
This systematic approach to feature prioritization will help your team make confident decisions about where to invest development resources, ensuring you build features that truly matter to both users and the business.